The Hindu: Page 04
Syllabus: GS 1: Art and Culture
After 46 years, the sacred treasury of Shree Jagannath Temple, Puri, known as Ratna Bhandar, was reopened amid years of legal battles, controversies, and debates.
About the Ratna Bhandar

- The Ratna Bhandar stores the gold and jewels offered by devotees to the deities Lord Jagannath, Lord Balabhadra, and Goddess Subhadra.
- It is located adjacent to the prayer hall on the north side of the temple.
- It consists of two sections: the ‘Bhitar Bhandar’ (Inner Treasury) and the ‘Bahar Bhandar’ (Outer Treasury), with the last inventory in 1978 noting significant amounts of gold and silver items in both chambers.
- Legend says, Odisha’s King Anangabhima Dev (1211 to 1238) donated 2.5 lakh madhas of gold to prepare jewellery for the almighty.
- The Odisha government passed the Jagannath Temple Act, 1952 to have a greater role in the temple’s management, which included maintaining an inventory of the offerings in the Puri collectorate’s Record Room.
Recent Developments:
- The safety of the Ratna Bhandar is managed by the Temple’s Committee, chaired by the titular ‘King of Puri’ and includes IAS officers and other state-appointed members.
- Originally, keys to the Ratna Bhandar were held by the Puri royal family, temple committee, and collectorate, with significant changes in ownership and access protocols over the years due to legal rulings.
- The recent reopening involved breaking the locks of the inner chamber as they could not be opened traditionally, following strict procedures.
About Jagannath Puri Temple
- The Jagannath Temple is an important Vaishnavite temple dedicated to Jagannath, a form of Sri Krishna in Puri in Odisha.
- The present temple was rebuilt from the 10th century onwards, on the site of an earlier temple, and begun by Anantavarman Chodaganga Deva, the first king of the Eastern Ganga dynasty.
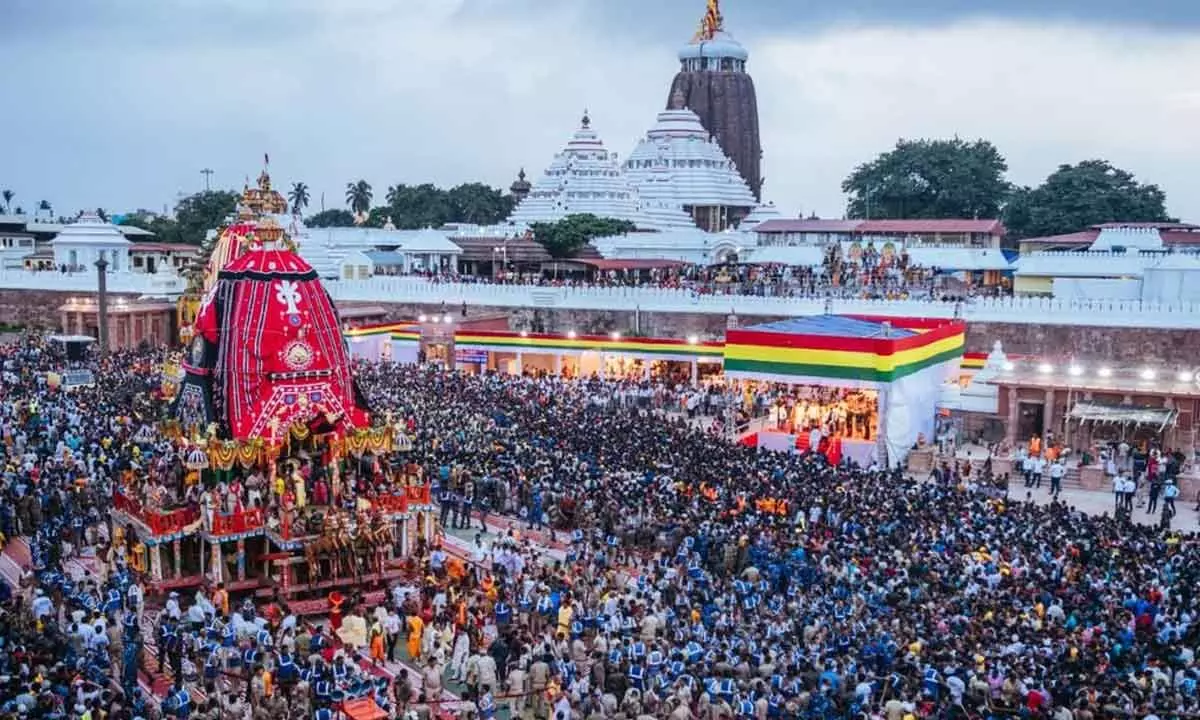
- The Puri temple is famous for its annual Ratha Yatra, or chariot festival, in which the three principal deities are pulled on huge and elaborately decorated temple cars.
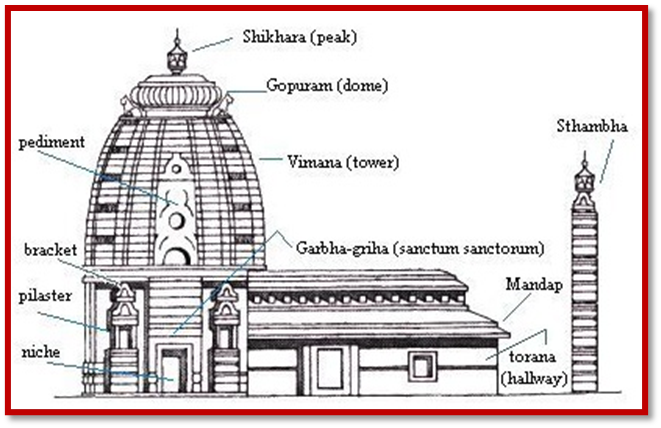
Its Architecture:
- With its sculptural richness and fluidity of the Oriya style of temple architecture, it is one of the most magnificent monuments of India.
- The huge temple complex covers an area of over 400,000 square feet and is surrounded by a high fortified wall.
- This 20 feet high wall is known as Meghanada Pacheri.
- Another wall known as kurma bedha surrounds the main temple.
The temple has four distinct sectional structures, namely:
1. Deula, Vimana or Garba griha (Sanctum sanctorum) where the triad deities are lodged on the ratnavedi (Throne of Pearls). In Rekha Deula style;
2. Mukhashala (Frontal porch);
3. Nata mandir/Natamandapa, which is also known as the Jagamohan (Audience Hall/Dancing Hall), and
4. Bhoga Mandapa (Offerings Hall)
Nabakalebar Festival
The Nabakalebar Festival is a significant and ancient religious event associated with the Jagannath Temple in Puri, Odisha
- Meaning: Symbolic renewal of Lord Jagannath’s wooden idols; Naba = new, Kalebara = body.
- Frequency: Occurs every 12-19 years based on lunar calendar alignment.
- Tree Selection: Sacred neem trees (Daru Brahma) are selected for new idols.
- Rituals: Old idols’ Brahma Padartha (soul) transferred to new idols in secret.
- Old Idol Disposal: Old idols are buried in Koili Baikuntha within the temple complex.
- Significant Event: Culminates with the famous Rath Yatra (Chariot Festival).
- Last Celebrated: 2015; next depends on lunar calendar conditions.
UPSC Prelims PYQ: 2012
Ques: The Nagara, the Dravida and the Vesara are the:
(a) Three main racial groups of the Indian subcontinent
(b) Three main linguistic divisions into which the languages of India can be classified
(c) Three main styles of Indian temple architecture
(d) Three main musical Gharanas prevalent in India
Ans: c)