The Hindu : Page 10
Syllabus : GS 3 : Indian Economy
The Karnataka government’s recent intent to introduce legislation for the welfare of gig workers is a necessary step to overcome the challenges to boost gig-economy in India.
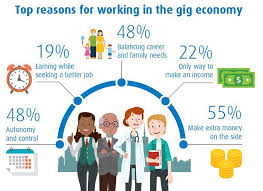
What is Gig Economy?
- As per the World Economic Forum (WEF), gig economy is defined by its focus on workforce participation and income generation via “gigs”, single projects or tasks for which a worker is hired.
- Gig economy includes all platformsthat hire independent workers across sectors like e-commerce, technology, food & beverages, home services among others.
- Gig workers are typically hired by companies on a contractual basisand are not considered employees. They do not receive some of the benefits that on-roll staffs do.
Classification: Gig workers can be broadly classified into:
- Platform workers: Those whose work is based on online software apps or digital platforms such as food aggregator platforms Zomato, Swiggy, Ola, and others.
- Non-platform-based workers: Casual wage and own-account workers in conventional sectors, engaged part-time or full-time.
Benefits of Gig Economy:
- For Workers: Gig economy can provide more flexibility, autonomy, income opportunities, skill development, and inclusion.
- For Employers: It can enable access to a large and diverse pool of talent, lower fixed costs, higher scalability, and better customer satisfaction.
- For Customers: It can offer more choice, convenience, quality, and affordability.
Current trend in the Indian Economy-
- about 47% of gig work is in medium skilled jobs
- about 22% in high skilled
- about 31% in low skilled jobs
- The trend shows the concentration of workers in medium skills is gradually declining and that of the low skilled and high skilled is increasing.
Expected trend:
- While in 2020-21, the gig workforce constituted 2.6% of the non-agricultural workforce or 1.5% of the total workforce in India, by 2029-30, gig workers are expected to form 6.7% of the non-agricultural workforce or 4.1% of the total livelihood workforce in India.
Why there is a need to regulate Gig- Economy?
- Due to non-permanent in nature: These jobs mainly have temporary contracts typically come with less protection, fewer benefits and pecuniary discounts.
- To bring gig-workers under Employment benefits protocol: The workers are mostly left out of the traditional social protection systems such as unemployment benefits, sick pay and pensions.
- Insurance and financial aids: Most transactions on the gig economy are done via the internet and as such they can be tracked. These companies do need to contribute to insurance and other social contributions.
- To reduce inequality of Income: Due to the increasingly complex supply chains and sub-contracting of gig jobs, make it hard to enforce protections. But without doing so we will not be able to combat the increasing levels of inequality.
UPSC Mains Practice Question
Ques : The gig economy has grown rapidly in India in recent years. In light of this statement discuss the challenges faced by gig workers in India and suggest ways to address them.







