The Karnataka government has formed an expert committee, headed by Niranjan, Chief Environment Officer of Karnataka State Pollution Control Board, to study the pollution level in the Cauvery.
About Cauvery River
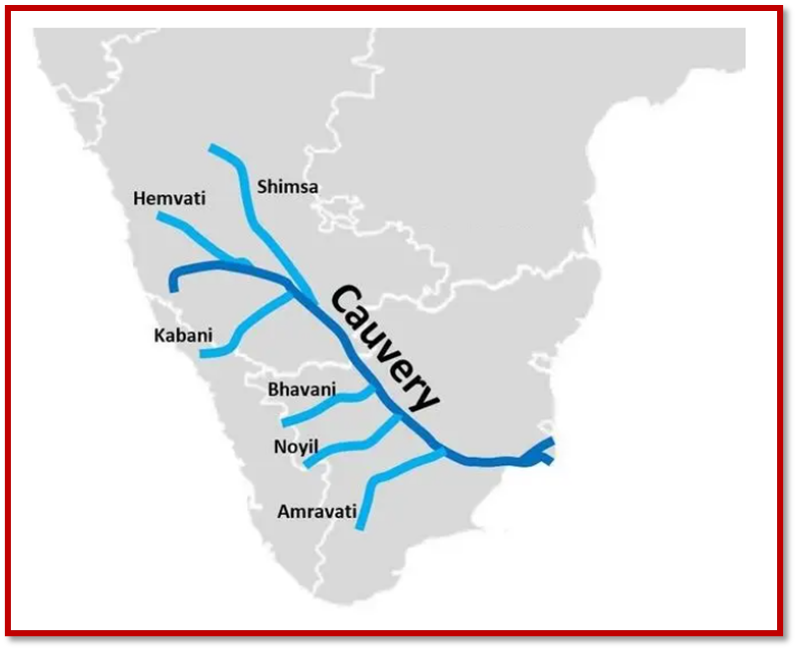
- The Cauvery River, also spelled as ‘Kaveri’ and known as ‘Ponni’ in Tamil, originates from Talakaveri in the Brahmagiri range located in Karnataka’s Kodagu district.
- It spans approximately 800 km, traversing through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, until it eventually reaches the Bay of Bengal.
- The river’s catchment area covers regions in Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, and the Union Territory of Pondicherry.
- Key tributaries that join the Cauvery include Harangi, Hemavati, Kabini, Suvarnavathi, and Bhavani.
- It remains perennial due to its dual reliance on both advancing and retreating monsoons for rainfall.
- Protected areas in its basin: Cauvery WLS, Biligirirangan Hills WLS, Pushpagiri WLS, Muthathi WLS, Ranganathittu Bird Sanctuary, Bhimeshwari WLS, Nagarhole NP; Bandipur NP.
About Niranjan Panel
- The panel will review and submit a report within 10 days to ascertain whether the Cauvery River water is polluted due to the inflow of sewage water, solid waste, industrial waste, and other types of pollutants.
- The Cauvery water has lost its natural quality due to the pollutants and the health of citizens and aquatic animals are being adversely affected.
Cauvery Water Dispute:
- Since 1892, tensions existed between British-ruled Madras and Mysore.
- 1924 Agreement aimed to resolve but set the stage for future conflicts. Post-Independence, dam constructions sparked TN appeal.
- Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal (CWDT) was established.
- Interim orders by the Cauvery River Authority (CRA) in 1998.
- CWDT’s 2013 award allocated water quantities among states.
- Monthly and annual water shares by Karnataka to Tamil Nadu.
- Normal Year, Karnataka must give 177.25 TMC to Tamil Nadu.
- Challenges arise during monsoons due to varying rainfall.
- Article 262 empowers Parliament for inter-state river disputes. The Seventh Schedule defines legislative authority over water resources.
- 2018: Cauvery was termed a “national asset” by SC with river water equality upheld.
- The Cauvery Management Board (CMB) was established by the Court for implementation.
- CWMA and CWRC were established for water regulation and data collection.