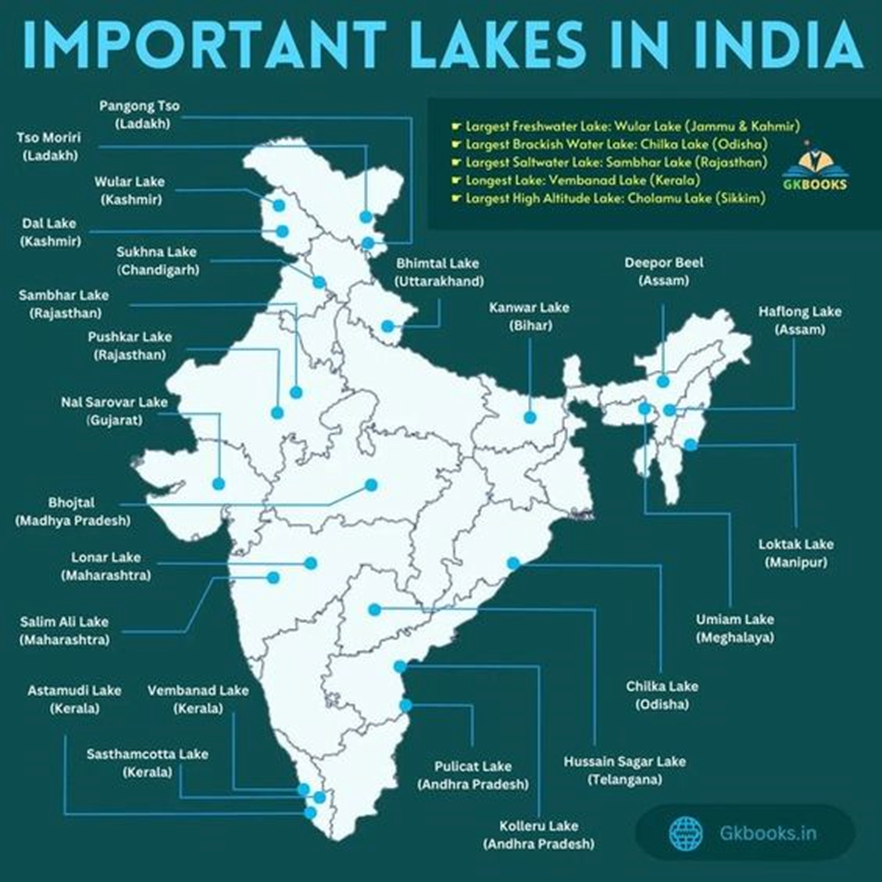
- A lake is a body of surface water bordered on all sides by land.
- Lakes will take water from rivers or function as a source of water since rivers will act as an outlet or inlet to them.
- Lakes may be found in a variety of settings, including hilly areas, plains, plateaus, rift zones, and so on.
- Some lakes are generated by the action of glaciers and ice sheets, while others are formed by wind, river movement, and human activity.
- Lakes are used for a variety of purposes, including drinking water, irrigation, navigation, water storage, livelihood (fishing, for example), and influence on microclimate.
- There are several sorts of lakes that may be classed depending on a variety of factors — these include:
- Freshwater Lakes,
- Salt Water lakes,
- Natural Lakes,
- Artificial Lakes,
- Oxbow lake,
- Crater Lake
Freshwater Lakes in India
- Freshwater lakes are produced in a variety of ways, and the microorganisms that survive and flourish in them are influenced by their formation.
- Stream or river-fed lakes, glacial lakes formed by melting glaciers, and man-made lakes created by the construction of a dam from abandoned mines or quarries are all typical types of lakes.
- In addition to modifying the microbiological makeup of a lake, stratification may cause a variation throughout the lake.
- The water in lakes is influenced by rain, snow, melting ice, streams, and groundwater seepage. Most lakes contain freshwater.
Important Fresh Water lakes in India