- A lake is a body of surface water bordered on all sides by land.
- Lakes will take water from rivers or function as a source of water since rivers will act as an outlet or inlet to them.
- Lakes may be found in a variety of settings, including hilly areas, plains, plateaus, rift zones, and so on.
- Some lakes are generated by the action of glaciers and ice sheets, while others are formed by wind, river movement, and human activity.
- Lakes are used for a variety of purposes, including drinking water, irrigation, navigation, water storage, livelihood (fishing, for example), and influence on microclimate.
- There are several sorts of lakes that may be classed depending on a variety of factors — these include:
- Freshwater Lakes,
- Salt Water lakes,
- Natural Lakes,
- Artificial Lakes,
- Oxbow lake,
- Crater Lake
Salt Water Lakes
- Due to the endorheic structure of the lake, the water pouring into the lake, which includes salt or minerals, is impossible to depart.
- The water then evaporates, leaving any dissolved salts behind and raising the lake's salinity, making it a perfect location for salt production.
- High salinity can also result in halophilic flora and fauna in and around the lake; in fact, the salt lake's lack of multicellular life is sometimes the result.
Important Salt Water lakes in India
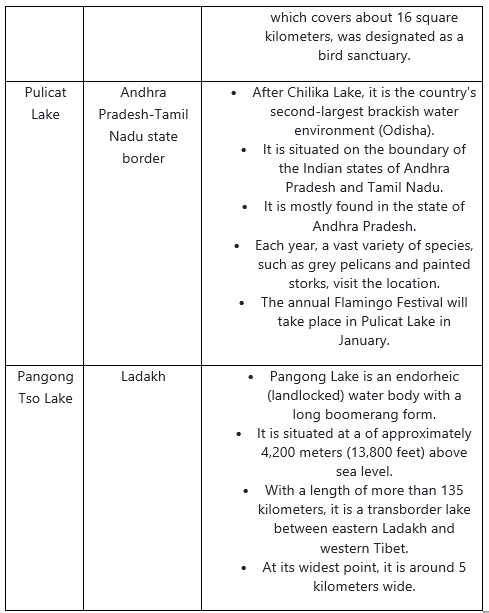
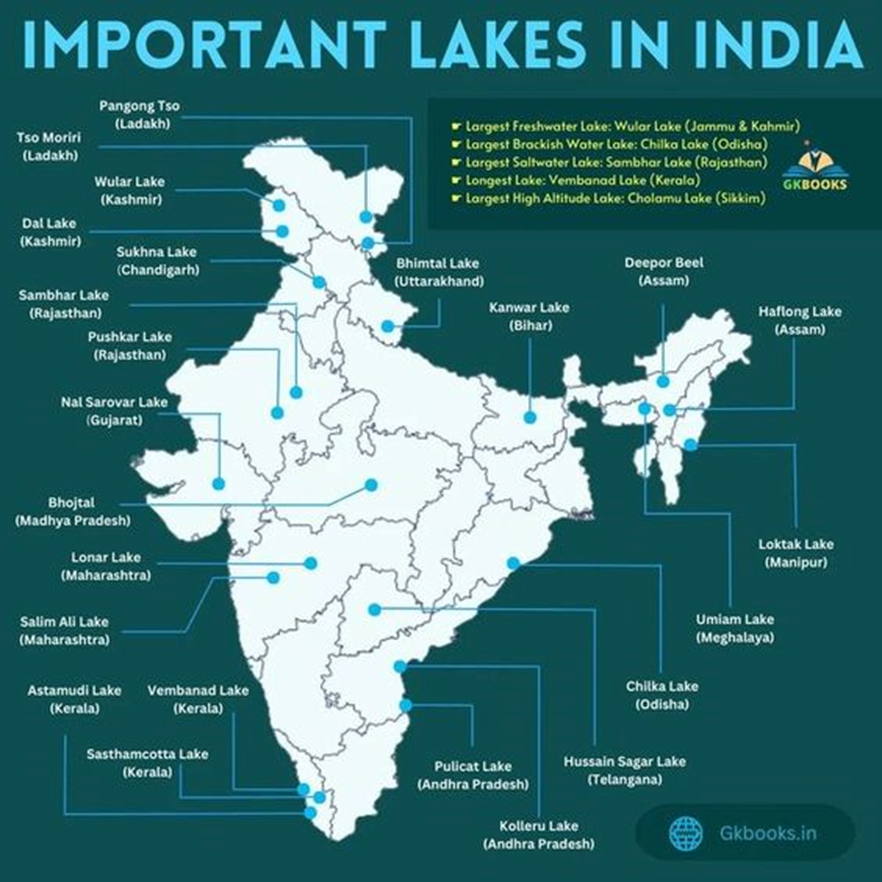
Natural Lakes in India
- Natural lakes can be found in mountainous locations, rift zones, and areas where glaciers still exist.
- The creation of natural lakes is aided by a number of factors.
- The tectonic movement of a mountain range can create bowl-shaped depressions that collect water and produce lakes.
- Landslides and glacial blocks cause lakes to form. Lagoons are formed by spits and bars along the shore.
Important Natural Lakes
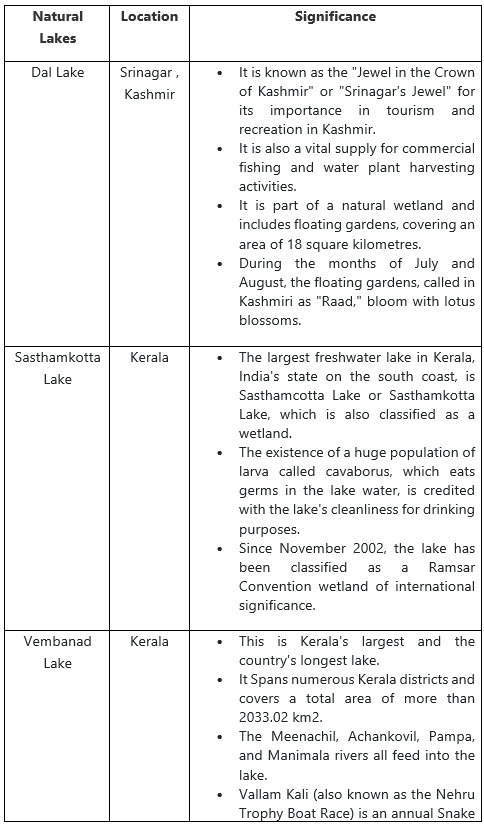
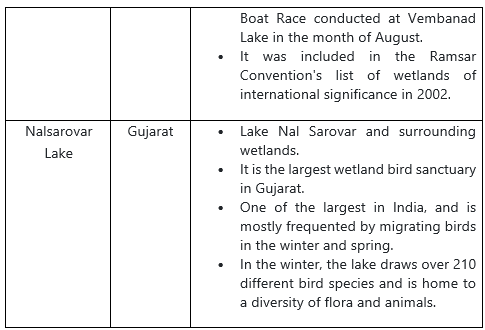
Oxbow Lakes
- Oxbow Lake is a small lake located in the abandoned meander loop of a river channel.
- A lake is generated by river bends that are U-shaped or curved and are cut off from the main river flow.
- Every river has its own set of twists and bends, also known as meanders, that cut through the landscape in a unique way.
- Due to continual erosion and deposition along the meanders' borders, the termination of the meander loop becomes closer and closer.
- The river meander loops finally cut themselves off, forming an oxbow lake.
Oxbow Lakes in India