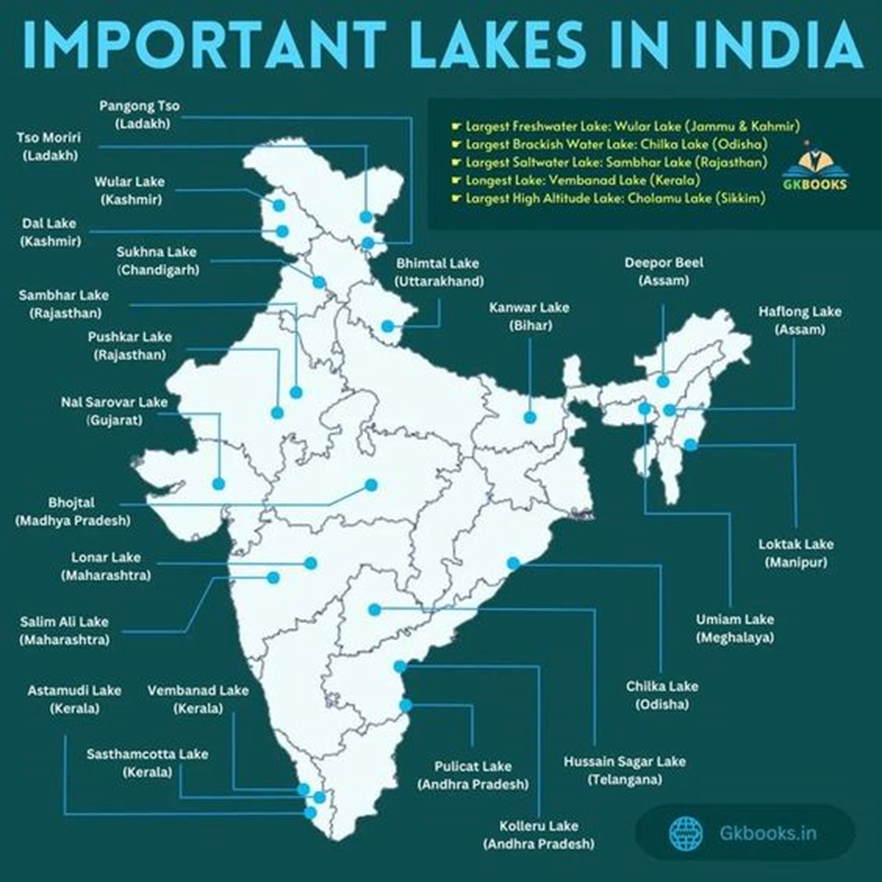
- A lake is a body of surface water bordered on all sides by land.
- Lakes will take water from rivers or function as a source of water since rivers will act as an outlet or inlet to them.
- Lakes may be found in a variety of settings, including hilly areas, plains, plateaus, rift zones, and so on.
- Some lakes are generated by the action of glaciers and ice sheets, while others are formed by wind, river movement, and human activity.
- Lakes are used for a variety of purposes, including drinking water, irrigation, navigation, water storage, livelihood (fishing, for example), and influence on microclimate.
- There are several sorts of lakes that may be classed depending on a variety of factors — these include:
- Freshwater Lakes,
- Salt Water lakes,
- Natural Lakes,
- Artificial Lakes,
- Oxbow lake,
- Crater Lake
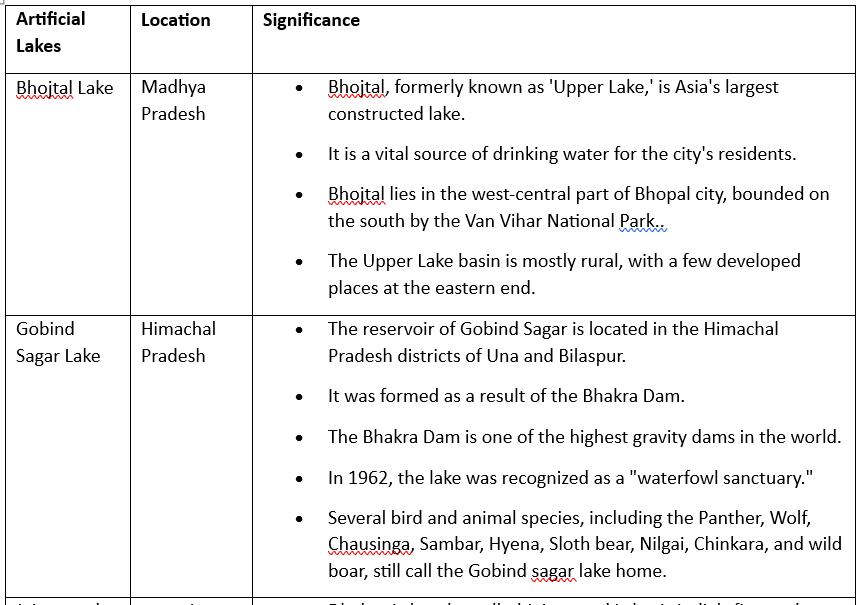
Artificial Lakes
- Artificial lakes, often known as reservoirs, are used all over the world as a source of water.
- Artificial lakes are frequently created by damming a section of a river and holding the water in a reservoir behind a dam.
- Throughout seasonal fluctuations, water flow and precipitation add to the reservoir, avoiding evaporation.
- They can also be built by excavating land or enclosing water using dykes.
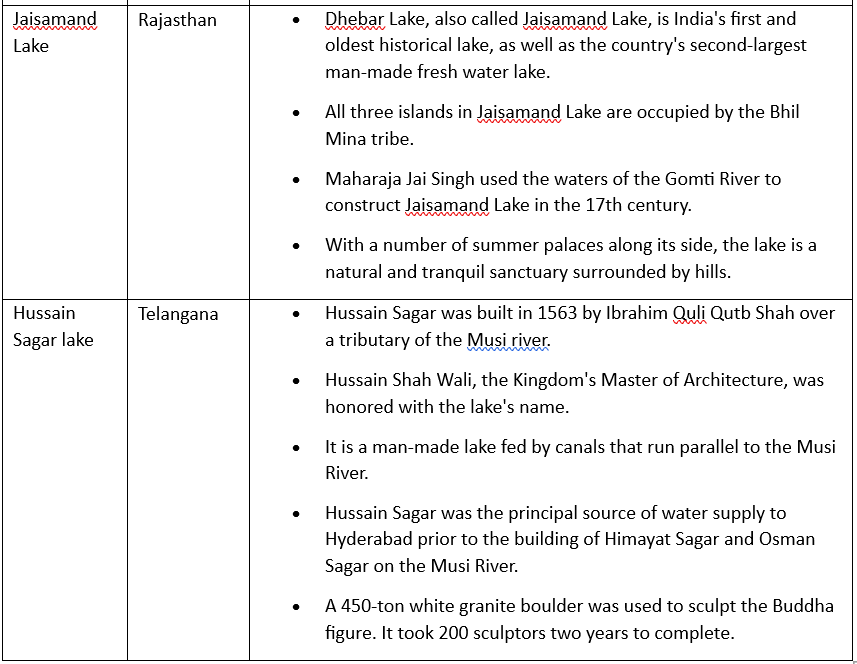
Artificial Lakes in India
Crater lake
- A volcanic crater or caldera creates a water-filled depression known as a crater lake.
- Lonar Lake is the best example of a crater lake in India. It's one of the planet's only four known hyper-velocity impact craters in basaltic rock.
- Water can come from precipitation, groundwater circulation, or melting glaciers.
- Its level rises until a balance is reached between the speeds of entering and departing water.
Lonar Lake
- Lonar Lake is the only known extraterrestrial impact crater and is found within the vast Deccan Traps, a large basaltic rock in India.
- The lake was originally considered to be volcanic, but it has now been shown to be an impact crater.
- A meteor or asteroid collided with Lonar Lake, forming the lake.
- Lonar Lake, also known as Lonar Crater, is a saline, soda lake located near Lonar in the Buldhana region of Maharashtra, India. It is a recognized National Geo-heritage Monument.
- Lonar Lake was produced by a meteorite collision event during the Pleistocene Epoch.
Significance of Lakes
- Lakes are significant for a variety of purposes, including controlling river flow, storing water during dry seasons, preserving the ecosystem, and producing hydroelectric power.
- The Himalayan area has the majority of freshwater lakes.
- They come from the ice age.
- To put it another way, they were formed when glaciers carved out a basin that was subsequently filled with snowmelt.
- A lake aids in the regulation of river flow.
- It reduces flooding following heavy rains and aids in maintaining a steady flow of water throughout the dry season.
- They assist to regulate the climate in the area, manage the aquatic habitat, increase natural beauty, promoting tourism, and offering recreation.