- They are the areas that are set by the government to conserve the natural environment.
- A national park has more restrictions as compared to a wildlife sanctuary.
- Their boundaries are fixed and defined.
- The main objective of a national park is to protect the natural environment of the area and biodiversity conservation.
What is allowed and what is not allowed inside National Parks:
- Here, no human activity is allowed.
- Grazing of livestock and private tenurial rights are not permitted here.
- Species mentioned in the Schedules of the Wildlife Act are not allowed to be hunted or captured.
- No person shall destroy, remove, or exploit any wildlife from a National Park or destroy or damage the habitat of any wild animal or deprive any wild animal of its habitat within a national park.
- They cannot be downgraded to the status of a ‘sanctuary’.
Declaration of National Parks:
- National parks can be declared both by the Central Government and State governments. No alteration of the boundaries of a national park shall be made except on a resolution passed by the State Legislature.
Important facts about the National Parks in India
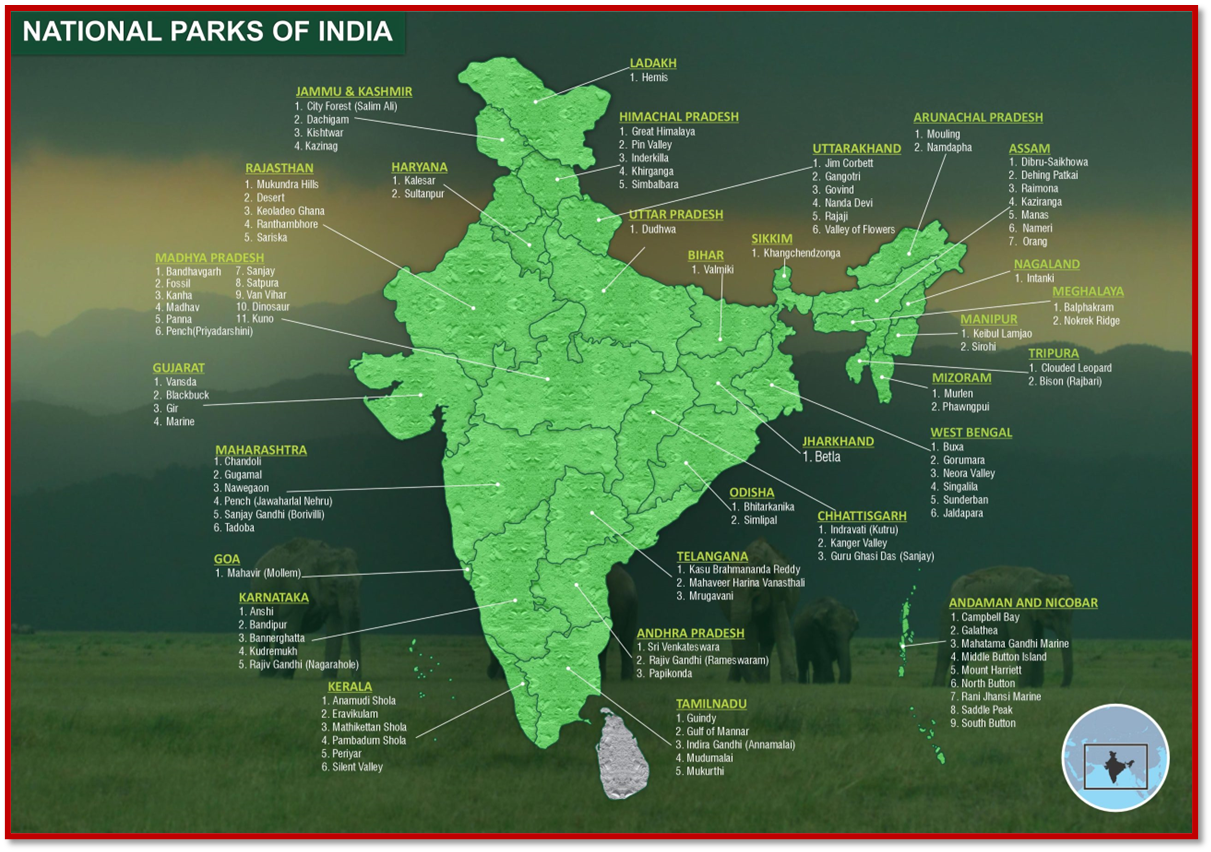
- Number of National 105
- Total area covered 40,501 sq.km.
- Maximum National Park state P. (9), Andaman & Nikobar (9)
- First National Park Jim Corbett National Park
- Largest National Park Hemis National Park
- Smallest National Park South Button National Park
- Latest National Park Kuno National Park
There are 104 existing national parks in India covering an area of 43,716 km2, which is 1.33% of the geographical area of the country
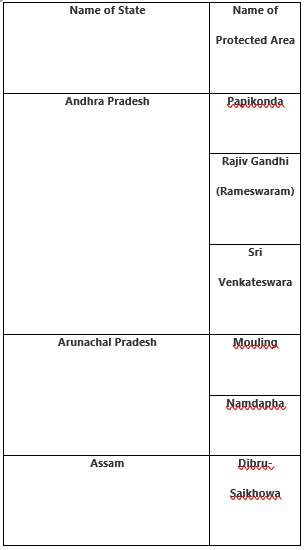
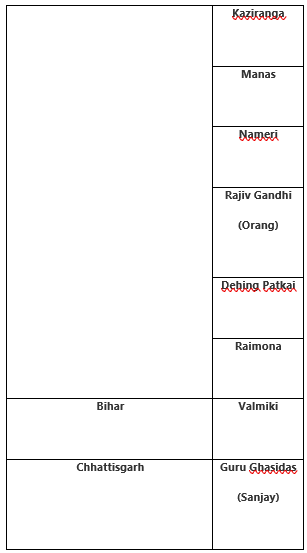
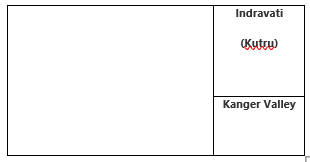
State-wise National Parks list