The Hindu: Page 04
Syllabus: GS 2: International Relations
Practice Question for Mains: India-Russia relations are crucial for India's strategic autonomy in a multipolar world." Evaluate the geopolitical importance of India-Russia relations in balancing India's ties with the West and China.

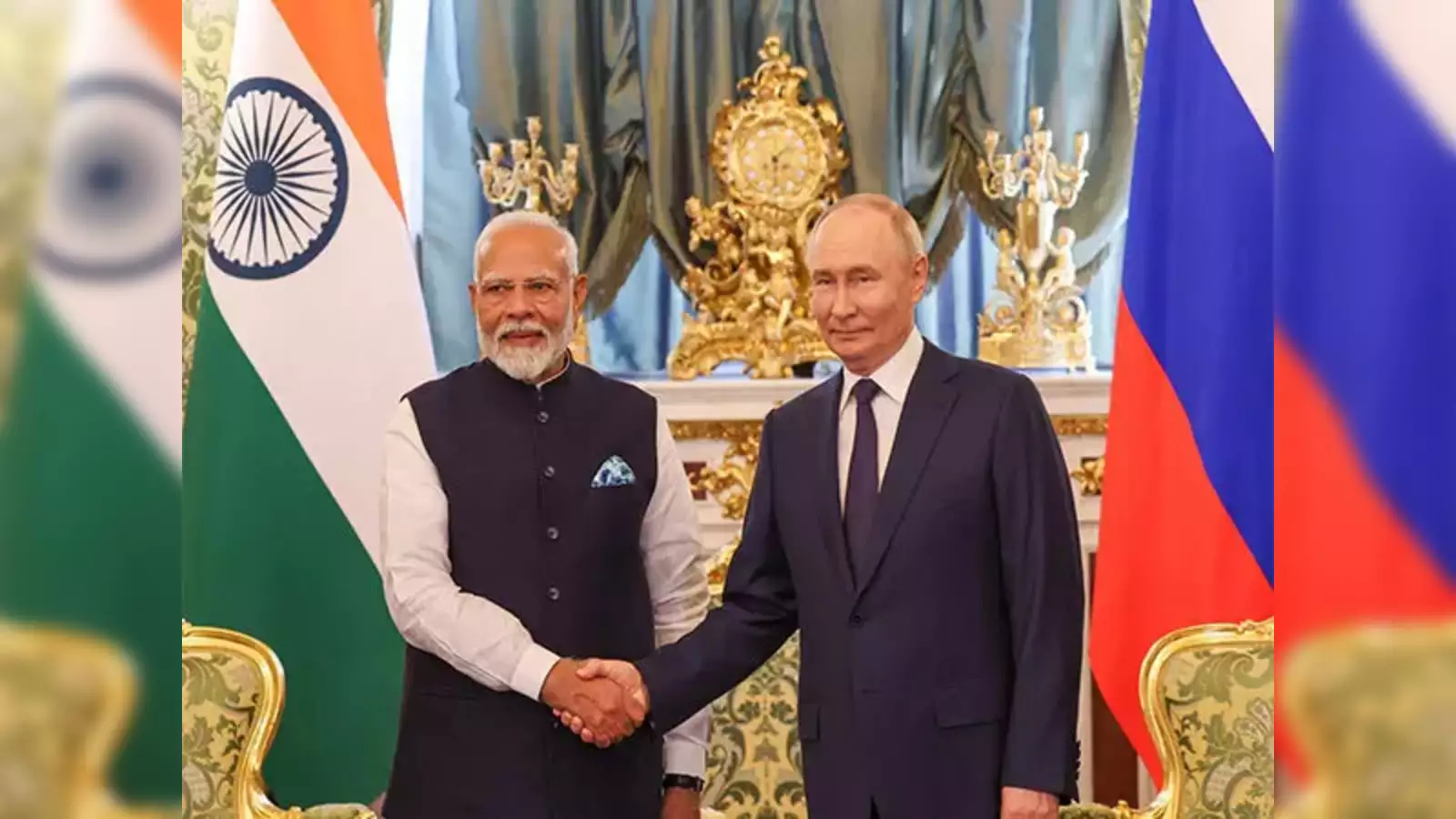
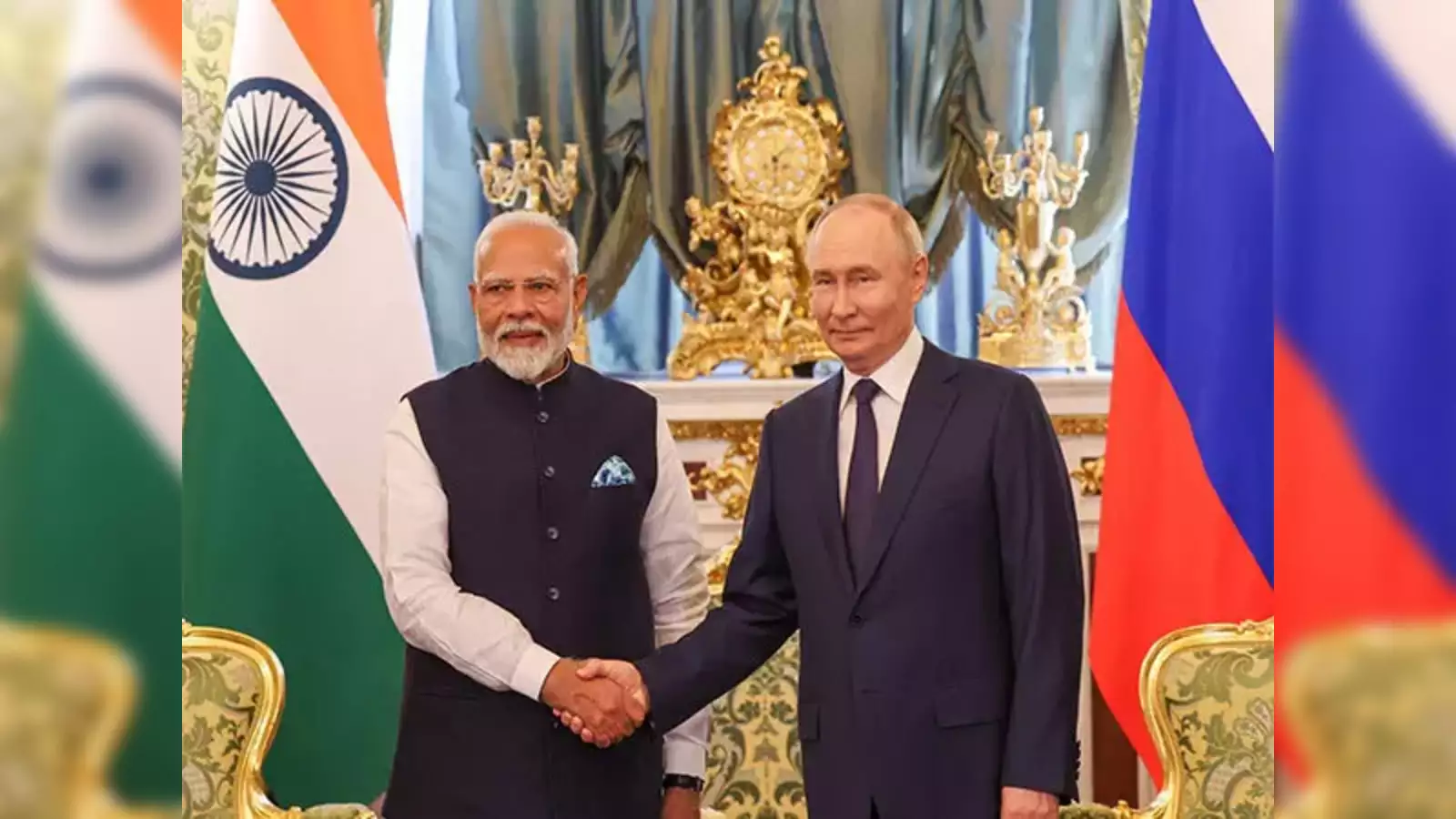
Sberbank notes rising trust in the Indian rupee despite sanctions, with transactions and rupee deposits surging.Prime Minister Modi’s Moscow visit aims at a $100 billion trade target by 2030, urging Indian firms to expand into sectors like auto, chemicals, and electronics in Russia.
India and Russia share a long-standing and strategic relationship that has evolved since the establishment of formal diplomatic ties in April 1947, just prior to India's independence. Historically, Russia (then the Soviet Union) has been a key partner for India, with the relationship shaping various aspects of India's foreign policy. The journey of India-Russia relations can be broken down into several phases:
The early relationship between newly independent India and the Soviet Union was marked by ideological differences, with limited interaction. Soviet leadership under Stalin was cautious, viewing India’s independence with suspicion. This dynamic began to shift in the mid-1950s, particularly with Indian Prime Minister Nehru's visit to Moscow in 1955 and Khrushchev’s reciprocal visit to India. These interactions led to significant projects like the establishment of the steel plants at Bhilai and Bokaro, symbolizing growing cooperation.
During the Cold War, India and the Soviet Union forged a strong diplomatic, military, and economic partnership. The USSR became a major arms supplier to India, playing a critical role during conflicts like the Sino-Indian War of 1962 and the Indo-Pak War of 1971. A landmark in bilateral ties was the 1971 Treaty of Peace, Friendship, and Cooperation, which included provisions for mutual consultations in the face of security threats. The relationship during this period was essential for India’s defense and geopolitical strategy.
After the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, the relationship weakened as both nations faced economic challenges and shifts in the global order. Despite the signing of the 1993 Treaty of Friendship and Cooperation, ties between India and Russia became strained, and collaboration in various sectors declined. The dissolution of the Soviet Union led to a period of readjustment in bilateral relations.
In 2000, the signing of the ‘Declaration on the India-Russia Strategic Partnership’ marked a turning point, elevating relations to a new level. This partnership has fostered closer cooperation in areas such as defense, trade, science, technology, and culture. The annual India-Russia Summit has served as a key mechanism for deepening engagement across these sectors.
India and Russia share close geopolitical ties, particularly through regional platforms like BRICS, the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), and the G20. India has maintained a balanced stance on contentious issues like Russia’s conflict with Ukraine, choosing not to participate in UN votes against Russia and continuing energy imports despite Western sanctions. Both nations advocate for a multipolar world order and jointly oppose terrorism in all its forms.
Russia remains a vital defense partner for India, supplying a significant portion of India’s military hardware. The defense relationship encompasses:
Bilateral trade and economic cooperation have grown significantly, with trade volumes reaching around $65 billion. India’s increased imports of discounted Russian crude oil, post-Ukraine war sanctions, have further strengthened this partnership. India also plays a role in the development of Russia’s Far East, providing financial and personnel assistance. A five-year cooperation program (2021-2025) is being finalized to bolster development in this resource-rich region.
Since the Cold War, scientific and research collaboration has been a key pillar of India-Russia relations. Key areas include:
Cultural ties between India and Russia remain strong, with Russian institutions offering courses in Hindi, Tamil, Marathi, and other Indian languages. Indian cultural organizations in Russia, such as the Indian Cultural Centre, promote cultural exchanges. The Indian diaspora in Russia, though small (30,000-40,000), plays a significant role in business and education.
Russia’s support for India on critical issues, such as its bid for a permanent seat in the UN Security Council and the Kashmir issue, enhances India’s strategic standing. In the context of rising Chinese aggression, Russia could also act as a stabilizing force, mitigating tensions between India and China.
Despite India diversifying its defense imports, Russia remains a crucial supplier of military equipment. With a significant portion of India’s defense inventory still of Russian origin, maintaining strong defense ties is essential, especially given China’s growing assertiveness on India’s borders.
India’s purchase of discounted Russian oil has helped cushion its economy against inflation caused by rising global crude prices. India is also exploring the possibility of a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the Eurasian Economic Union, which could further boost trade ties.
India’s balanced relationship with Russia provides it with greater leverage in negotiations with Western powers. It also helps offset China’s influence in Eurasia, ensuring that India can navigate the complexities of great power competition without compromising its national interests.
UPSC Prelims PYQ : 2019
Ques : Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries?
(a) Japan
(b) Russia
(c) The United Kingdom
(d) The United States of America
Ans: b)