The Hindu: Page 11
Syllabus: Science and Technology
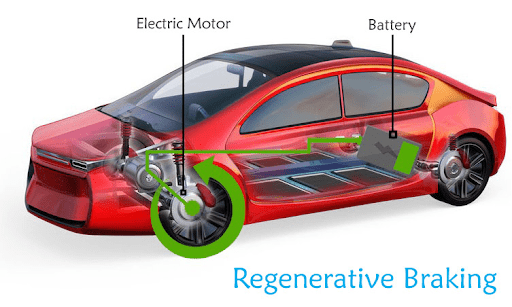
Regenerative Braking System
Definition:
- A regenerative braking system is a technology used in electric and hybrid vehicles to recover kinetic energy that would otherwise be lost during braking. The system converts this kinetic energy into electrical energy, which can then be stored in the vehicle’s battery and reused.
Traditional Braking System vs. Regenerative Braking:
- Traditional Braking: When brakes are applied, the kinetic energy of the vehicle is converted into heat due to friction and is dissipated into the environment, resulting in energy loss.
- Regenerative Braking: Converts the vehicle’s kinetic energy into electrical energy during braking, which is stored in the battery or supercapacitor for later use, thus reducing energy waste.
How Regenerative Braking System Works:
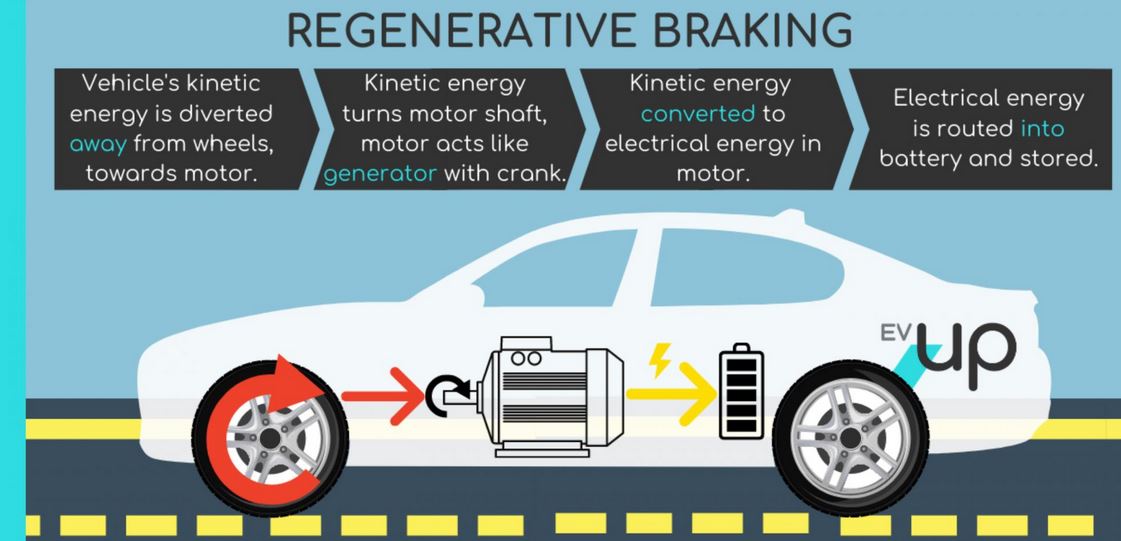
- Kinetic Energy Conversion: As the vehicle moves, it possesses kinetic energy. When the driver applies the brakes, the regenerative braking system activates.
- Motor as a Generator: The electric motor, which usually drives the wheels, reverses its function during braking and acts as a generator. It converts the vehicle’s kinetic energy into electrical energy.
- Energy Storage: The electrical energy generated is stored in the vehicle’s battery or a supercapacitor, depending on the vehicle’s design.
- Energy Reuse: The stored energy is used to power the vehicle, reducing the need for external power sources and enhancing the vehicle’s efficiency.
Benefits of Regenerative Braking:
- Improved Energy Efficiency: Recovers energy that would otherwise be wasted and reduces overall energy consumption, thereby enhancing vehicle efficiency.
- Reduced Emissions: Minimizes heat generation during braking, leading to reduced environmental impact.
- Reduced Wear and Tear: Less dependence on traditional friction brakes reduces wear and tear on brake components, leading to lower maintenance costs.
Limitations of Regenerative Braking:
- Efficiency Drops at Lower Speeds: The amount of kinetic energy available for conversion decreases as the vehicle slows down, making the system less efficient at lower speeds.
- Not a Complete Replacement for Conventional Brakes: Regenerative braking systems cannot bring the vehicle to a complete stop on their own. Conventional friction brakes are still required for complete braking and emergency stops.
Applications:
- Widely used in electric and hybrid vehicles to enhance energy efficiency.
- The technology can also be applied in bicycles, trains, and even industrial machinery to conserve energy.
Conclusion:
- The regenerative braking system is a significant advancement in automotive technology, contributing to increased energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact. However, its limitations require it to work in conjunction with traditional braking systems to ensure complete vehicle control and safety.