The Hindu : Page 03
Syllabus : GS 3 : Agriculture & Science and Technology

Kerala’s pearl spot farmers face slow growth rates and production challenges, prompting the Kerala University of Fisheries and Ocean Studies (Kufos) to launch a genome editing mission.
- This initiative aims to enhance growth rates and breeding efficiency, potentially revolutionising pearl spot aquaculture, which has high market demand and value.
- The Kerala University of Fisheries and Ocean Studies (Kufos) plans a genome editing mission to enhance pearl spot growth rates, similar to the success of genetically improved farmed tilapia (GIFT).
Genome Editing
- Genome editing (also called gene editing) is a group of technologies that give scientists the ability to change an organism's Deoxy-Ribonucleic Acid (DNA).
- These technologies allow genetic material to be added, removed, or altered at particular locations in the genome
Pros of Gene editing
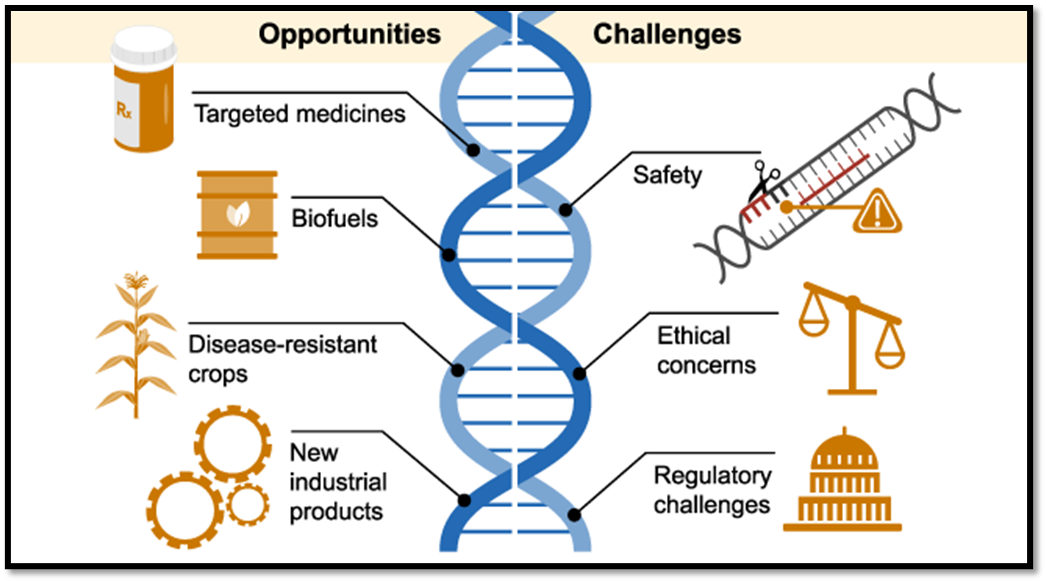
- CRISPR could be used to modify disease-causing genes in embryos brought to term, removing the faulty script from the genetic code of that person’s future descendants as well. Genome editing (Gene editing) could potentially decrease, or even eliminate, the incidence of many serious genetic diseases, reducing human suffering worldwide.
- It might also be possible to install genes that offer lifelong protection against infection.
Cons of Gene editing
- Making irreversible changes to every cell in the bodies of future children and all their descendants would constitute extraordinarily risky human experimentation.
- There are issues including off-target mutations (unintentional edits to the genome), persistent editing effects, genetic mechanisms in embryonic and fetal development, and longer-term health and safety consequences.
- Some argue that we do not understand the operations of the genome enough to make long-lasting changes to it. Altering one gene could have unforeseen and widespread effects on other parts of the genome, which would then be passed down to future generations.
- Many consider genome alterations to be unethical, advocating that we should let nature run its course.
- Few argue that permitting human germline gene editing for any reason would likely lead to its ignorance of the regulatory limits, to the emergence of a market-based eugenics that would exacerbate already existing discrimination, inequality, and conflict.
- It will become a tool for selecting desired characteristics such as intelligence and attractiveness.
Genome editing – It’s benefits for agriculture and animal husbandry:
- Definition of Genome Editing: Genome editing is a precise molecular technique that allows scientists to make targeted changes to an organism’s DNA, enabling modifications to specific genes with accuracy.
- Benefits of Genome Editing for Agriculture: Crop Improvement: Genome editing can enhance crop traits such as yield, nutrition, and resistance to pests and diseases.
- Precision Breeding: It offers a more precise alternative to traditional breeding methods, accelerating the development of desirable traits in crops/animals.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: By enhancing disease resistance, crops may require fewer pesticides and fungicides, reducing chemical usage and environmental pollution.
- Climate Resilience: Editing genes can help crops adapt to changing climatic conditions, such as drought or extreme temperatures, ensuring agricultural productivity.
- Nutritional Enhancement: Editing can enrich crops with essential nutrients, addressing malnutrition issues globally.
- Faster Development: Compared to traditional breeding, genome editing can shorten the time required to develop new crop varieties with improved traits.
- Potential for Sustainable Agriculture: It supports sustainable farming practices by reducing resource inputs while maintaining or increasing crop productivity.
PYQ UPSC Prelims : (2019)
Ques. What is Cas9 protein that is often mentioned in news?
a) A molecular scissors used in targeted gene editing
b) A biosensor used in the accurate detection of pathogens in patients
c) A gene that makes plants pest-resistant
d) A herbicidal substance synthesized in genetically modified crops
Ans: (a)