The Hindu: Page 03
Syllabus: GS 3: Infrastructure
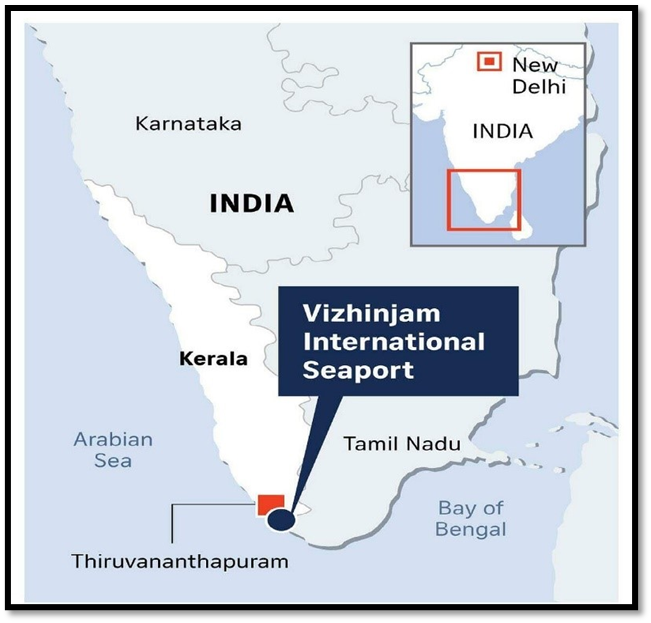
The first cargo-carrying mothership from Xiamen, China, docked at India’s Vizhinjam international seaport on Thursday morning.
- Vizhinjam is India’s first deep-water container transshipment port.
- The container ship San Fernando, flagged by the Marshall Islands and managed by Bernhard Schulte Ship Management, carried 1,930 containers.

What is a mothership?
- A mothership is a large vessel or aircraft that carries, launches, or supports smaller vehicles or vessels.
- In maritime contexts, it typically refers to a large ship that provides logistical support, housing, and transportation for smaller boats or submarines.
- Motherships are crucial in various operations, including military, exploration, and commercial activities.
- They offer facilities like maintenance, supplies, and crew quarters for the smaller crafts they support.
Deepwater transshipment port
Deepwater port
- A deepwater port is a manmade structure that are used as ports or terminals to transport, store, or handle oil or natural gas.
- These structures can be fixed or floating, and are located beyond state seaward boundaries.
- They can include: Pipelines, Pumping stations, Service platforms, Mooring buoys.
Transshipment port
- A transshipment port is a port where goods are offloaded and loaded onto a different ship to continue their journey to their final destination.
Vizhinjam port: Vizhinjam port is India’s first international deepwater transshipment port.
Some of the special features are:
- Unique Depth: Vizhinjam boasts a natural depth of over 18 meters, expandable to 20 meters, making it capable of accommodating large vessels and mother ships.
- Versatile Purpose: The port is designed to handle container transshipment, multi-purpose, and break-bulk cargo. It is strategically located just ten nautical miles from the international shipping route.
- Low Maintenance: The port has minimal littoral drift and requires minimal maintenance dredging, reducing operational costs.
- Competitive Advantage: Vizhinjam aims to compete with transshipment hubs like Colombo, Singapore, and Dubai. It is expected to reduce container movement costs to and from foreign destinations.
- Initial Capacity: The first phase of the project has a capacity of one million TEU (twenty-foot equivalent units), which can be expanded to 6.2 million TEU.
- Job Opportunities: The project is expected to create 5,000 direct job opportunities, support industrial growth, and boost cruise tourism.
- Advanced Infrastructure: Vizhinjam offers state-of-the-art automation and infrastructure to handle Megamax container ships efficiently.
Major Ports in India
India has 13 major ports, which are governed by the central government under the Major Port Authorities Act, 2021. These ports play a crucial role in international trade and serve as the primary gateways for cargo transportation. The major ports in India are:
- Mumbai Port (Maharashtra)
- Jawaharlal Nehru Port (Nhava Sheva) (Maharashtra)
- Chennai Port (Tamil Nadu)
- Kolkata Port (Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port) (West Bengal)
- Haldia Port (West Bengal)
- Visakhapatnam Port (Andhra Pradesh)
- Paradeep Port (Odisha)
- Kandla Port (Deendayal Port) (Gujarat)
- Cochin Port (Kerala)
- New Mangalore Port (Karnataka)
- Tuticorin Port (V.O. Chidambaranar Port) (Tamil Nadu)
- Mormugao Port (Goa)
- Ennore Port (Kamarajar Port) (Tamil Nadu)
Legal Criteria to Differentiate Between Major and Minor Ports
The distinction between major and minor ports in India is governed by the Indian Ports Act, 1908, and the Major Port Authorities Act, 2021. The key differences are:
Governance and Regulation:
- Major Ports: Governed by the central government through the Major Port Authorities Act, 2021. The Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways is responsible for their administration, policy formulation, and regulation.
- Minor Ports: Governed and administered by the respective state governments as per the Indian Ports Act, 1908. The state governments have the authority to regulate, develop, and maintain these ports.
Sagarmala Initiative: Overview and Key Details
Sagarmala is a flagship program of the Government of India aimed at harnessing the potential of India’s 7,500 km coastline and 14,500 km of navigable waterways for port-led development. Launched in 2015, the initiative focuses on promoting port-led prosperity, enhancing logistics efficiency, and boosting trade.
Objectives of Sagarmala
Port Modernization and New Port Development:
- Improve operational efficiency and capacity of existing ports.
- Develop new deep-sea ports to accommodate large vessels.
- Upgrade port infrastructure with modern equipment and technology.
Port Connectivity Enhancement:
- Improve connectivity to ports through road, rail, and inland waterways.
- Develop multi-modal logistics solutions to streamline the supply chain.
- Establish new Coastal Economic Zones (CEZs) linked to ports for better integration.
Port-Linked Industrialization:
- Promote manufacturing and processing industries around port areas.
- Create Coastal Employment Units (CEUs) to generate employment.
- Develop CEZs focusing on petrochemical clusters, electronics, apparel, and auto manufacturing.
Coastal Community Development:
- Improve socio-economic conditions of coastal communities.
- Implement skill development programs for local populations.
- Promote sustainable fisheries, tourism, and other coastal industries.
Coastal Shipping and Inland Water Transport (IWT):
- Promote coastal shipping as an eco-friendly and cost-effective transport mode.
- Develop Inland Water Transport to reduce pressure on road and rail networks.
Key Projects under Sagarmala
- Port Modernization Projects: Projects like deepening channels, mechanizing berths, and increasing cargo handling capacities at major and minor ports.
- Port Connectivity Projects: Initiatives such as the Dedicated Freight Corridor, coastal berths, road connectivity projects, and the development of multi-modal logistics parks.
- Inland Waterways Projects: Development of National Waterways (e.g., NW-1 on the Ganga-Bhagirathi-Hooghly river system).
- Industrial Cluster Projects: Establishment of CEZs along the coastal regions to boost industrial growth and exports.
- Skill Development Projects: Training and skill enhancement programs for coastal communities to ensure inclusive growth.
Key Achievements
- Over 574 projects with an estimated cost of ₹6.01 lakh crores have been identified.
- Multiple projects have been completed, including the construction of new berths, road and rail connectivity improvements, and the establishment of new ports.
- Increased coastal shipping tonnage and improved efficiency of port operations, reducing logistics costs for industries.
Expected Benefits
- Reduction in logistics cost for EXIM (export-import) and domestic trade.
- Creation of employment for millions of people in coastal regions.
- Boost to the Indian economy through enhanced trade, reduced turnaround time at ports, and improved ease of doing business.
Challenges Faced
- Coordination between various government agencies.
- Environmental concerns due to port expansion and industrial activities.
- Financing and timely execution of large-scale projects.
Government Policies and Support
The Sagarmala initiative is supported by several policies such as the National Maritime Development Programme and various incentives for coastal shipping, including subsidies for Ro-Ro (Roll on-Roll off) vessels and dedicated freight corridors to improve port connectivity.