The Hindu : Page 07
Syllabus GS: 02 : Governance and Social Justice
Context :
- A recent article in the Lancet has once again turned the spotlight on suicide. Psychiatrists have been talking about ways to reduce suicides but rue the fact that governments, state and central, have shown little interest.
Strategy to curb suicides
- A blueprint to stem suicides, the National Suicide Prevention Strategy, was launched in November 2022.
- The aim was to establish effective surveillance mechanisms for suicide within three years and establish psychiatric outpatient departments to provide suicide prevention services through the District Mental Health Programmes in all districts within the next five years.
- It called for integrating a mental well-being curriculum into all educational institutions within eight years.
- It also sought to develop guidelines for responsible media reporting of suicides and restrict access to the means for suicide.
Top killer
- In India, more than 1 lakh lives are lost annually to suicide, and it is the top killer in the 15-29 years category.
- From 2019 to 2022, the suicide rate increased from 10.2 to 11.3 per 1,00,000.
- The NSSP envisages a specific strategy for every state and district.
- The ministry of health, education, and agriculture in each state must have a task force.
- The health department should take the lead, but other departments like fertilisers, chemicals, information and broadcasting should also be represented in the task force.
- The education department should be included to promote emotional wellbeing.
- Soumitra Pathare, Director for Centre for Mental Health Law and Policy, one of the framers blames lack of political will.
‘Sense of fatality’
- There is a sense of fatality when we start talking about suicide prevention. Even a 20% drop in suicides would save 40,000 lives annually.
- The lack of will in the media to make conscientious efforts to educate themselves on reporting suicides.
- By talking about suicides we would be acknowledging the problem and try to find solutions.
- The present approach is piecemeal. We need a district wise programme that can bring about consistent results.
- The National Education Policy is good, but it has not been implemented.
- The vocational guidance programme and multiple exits, grade system, and the flexibility to make course changes are all good. But it has not been implemented.
- The policy changes do make a difference and these policies are there and need to be implemented.
- Tieing up NEP and NSPS, and by implementing the strategies deaths can be reduced.
Way forward
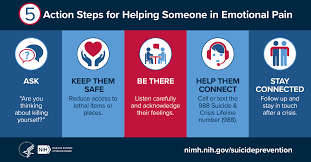
- Suicides can be prevented with timely supportive action. Citizens must learn the skills of identifying someone with suicidal thoughts, asking them openly about their thoughts, talking to them without fear, and referring them to a caregiver who can complete a safety plan and provide suicide prevention counselling.
- These steps, if taken with care person, can save many lives at risk.
What is suicide?
- Suicide is when people harm themselves with the goal of ending their life, and they die as a result.
- A suicide attempt is when people harm themselves with the goal of ending their life, but they do not die.
Data on suicide deaths in India:
- In India, more than one lakh lives are lost every year to suicide, and it is the top killer in the 15-29 years category.
- In the past three years, the suicide rate has increased from 10.2 to 11.3 per 1,00,000 population, the document records.
- The most common reasons for suicide include family problems and illnesses, which account for 34% and 18% of all suicide-related deaths.
Treatments and Therapies:
Brief Interventions
o Personalized safety planning has been shown to help reduce suicidal thoughts and actions.
o Research has shown that when at-risk patients receive further screening, a Safety Plan intervention, and a series of supportive phone calls, their risk of suicide goes down.
Psychotherapies:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
o It can help people learn new ways of dealing with stressful experiences.
o CBT helps individuals recognize their thought patterns and consider alternative actions when thoughts of suicide arise.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT):
o It has been shown to reduce suicidal behavior in adolescents.
India’s First Suicide Prevention Policy
In 2022, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare announced a National Suicide Prevention Strategy.
More about the policy
o The newly launched National Suicide Prevention Strategy is the first of its kind in the country.
o The suicide prevention policy comes with time-bound action plans and multi-sectoral collaborations to achieve reduction in suicide mortality by 10% 2030.
o The strategy broadly seeks to:
- Establish effective surveillance mechanisms for suicide within the next three years,
- Establish psychiatric outpatient departments that will provide suicide prevention services through the District Mental Health Programme in all districts within the next five years, and
- To integrate a mental well-being curriculum in all educational institutions within the next eight years.
o The policy envisages:
- Developing guidelines for responsible media reporting of suicides, and
- Restricting access to means of suicide.
o Community & societal support:
- The stress is on developing community resilience and societal support for suicide prevention.
- In line with global strategy:
- The UN’s Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3.4 aims to reduce premature mortality from non-communicable diseases by one-third, through prevention and treatment, and promote mental health and well-being.
- One of the indicators for this is the suicide rate.
- While the strategy is in line with the WHO’s South East-Asia Region Strategy for suicide prevention, it says it will remain true to India’s cultural and social milieu.
Government of India Initiatives
- National Mental Health Programme (NMHP), 1982:
o To ensure the availability and accessibility of minimum mental healthcare for all in the foreseeable future, particularly to the most vulnerable and underprivileged sections of the population.
- Mental Healthcare Act, 2017 – Decriminalising suicide attempts:
o It was passed in 2017, came into effect in May 2018 and replaced the Mental Health Act of 1987.
o To the joy of most Indian medical practitioners and advocates of mental health, the act decriminalised suicide attempts in India.
o It also included WHO guidelines in the categorisation of mental illnesses.
o The most significant provision in the act was “advanced directives”, which allowed individuals with mental illnesses to decide the course of their treatment and also appoint someone to be their representative.
o It also restricted the use of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), and banned its use on minors, finally introducing measures to tackle stigma in Indian society.
Manodarpan Initiative:
- It is an initiative under Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan.
- It aims to provide psyho-social support to students for their mental health and well-being.
Kiran Helpline:
- The helpline is a giant step towards suicide prevention, and can help with support and crisis management.
- The helpline aims to provide early screening, first-aid, psychological support, distress management, mental well-being, and psychological crisis management and will be managed by the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD).
Issues & way ahead
- Focus not up to the mark:
o The recent National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) report stated that 1.64 lakh people died by suicide in 2021.
o This is 10 per cent higher than the COVID deaths in India 2020, and 6.8 times the maternal death (23800) in 2020.
o Yet, we have had so much more focus and efforts on COVID protocols and maternal health as compared to suicide prevention.
- Need for collaborative efforts:
o Given that suicide is a complex issue, tackling it will necessarily require inter-sectoral collaboration.
o The 2021 NCRB data shows that family issues (33.2 per cent), unemployment/indebtedness/career problems (7.7 percent), health concerns (18.6 percent) are some of the major causes.
o To work on prevention, we need the Ministry of Women and Child Development, Ministry of Commerce & Industry, the MoHFW, among others, to work collaboratively.
- Requirement of an effective implementation:
o The strategy should now be passed on to the States for them to develop locally relevant action plans; and then cascade to the district, primary health and community levels.
o Further efforts are now required to prevent suicides as a public health priority.
o Suicides impact all sections of the society and thus require concerted and collaborative efforts from individuals and the community at large.